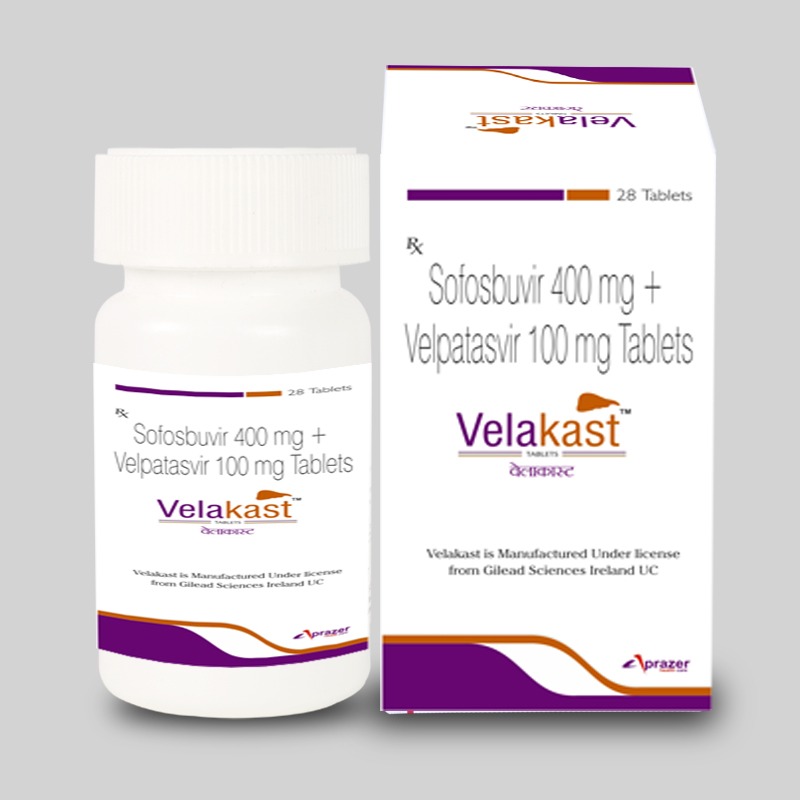
VELAKAST- Sofosbuvir 400mg and Velpatasvir 100mg
VELAKAST is a fixed-dose combination tablet containing sofosbuvir and velpatasvir for oral administration. Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide analog HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor and velpatasvir is an NS5A inhibitor. Each tablet contains 400 mg sofosbuvir and 100 mg velpatasvir. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: Titanium Dioxide IP and Brilliant Blue FCF, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Effect of the drug (Velakast)
Thanks to the powerful composition of the drug, Velakast APRAZER HEALTHCARE is widely used to fight the hepatitis C virus of genotypes 1-6. The drug may be given as a monotherapy or for combined treatment with or without cirrhosis. The high effectiveness of the drug against all genotypes of HCV is due to the presence in its composition.
Sofosbuvir: The IUPAC name for sofosbuvir is (S)-Isopropyl 2-((S)-(((2R,3R,4R,5R)-5(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin- 1(2H)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran- 2yl)methoxy (phenoxy)phosphorylamino)propanoate. It has a molecular formula of C22H29FN3 O9 P and a molecular weight of 529.45. Sofosbuvir is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a solubility of at least 2 mg/mL across the pH range of 2–7.7 at 37°C and is slightly soluble in water. – www.galaxysuperspeciality.com
Velpatasvir: The IUPAC name for velpatasvir is Methyl {(1R)-2-[(2S,4S)-2-(5-{2[(2S,5S)-1-{(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl) amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}-5-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]1,11-dihydro[2]benzopyrano[4′,3′:6,7]naphtho[1,2-d]imidazol-9- yl}-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-4(methoxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl}carbamate. It has a molecular formula of C49H54 N8 O8 and a molecular weight of 883.0. Velpatasvir is practically insoluble (less than 0.1 mg/mL) above pH 5, slightly soluble (3.6 mg/mL) at pH 2, and soluble (greater than 36 mg/mL) at pH 1.2.
Mechanism of Action (Velakast)
VELAKAST is a fixed-dose combination of sofosbuvir and velpatasvir which are direct-acting antiviral agents against the hepatitis C virus Sofosbuvir is an inhibitor of the HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which is required for viral replication. Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide prodrug that undergoes intracellular metabolism to form the pharmacologically active uridine analog triphosphate (GS-461203), which can be incorporated into HCV RNA by the NS5B polymerase and acts as a chain terminator. In a biochemical assay, GS-461203 inhibited the polymerase activity of the recombinant NS5B from HCV genotype 1b, 2a, 3a and 4a with an IC50 value ranging from 0.36 to 3.3 micromolar. GS-461203 is neither an inhibitor of human DNA and RNA polymerases nor an inhibitor of mitochondrial RNA polymerase. Velpatasvir is an inhibitor of the HCV NS5A protein, which is required for viral replication. Resistance selection in cell culture and cross-resistance studies indicates velpatasvir targets NS5A as its mode of action.
Pharmacodynamics
The effect of sofosbuvir 400 mg (recommended dosage) and 1200 mg (three times the recommended dosage) on QTc interval was evaluated in an active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) thorough QT trial. At a dose three times the recommended dose, sofosbuvir does not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent. The effect of velpatasvir 500 mg (five times the recommended dosage) was evaluated in an active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) thorough QT trial. At a dose five times the recommended dose, velpatasvir does not prolong QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VELAKAST is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic Hepatitis C Virus, Genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection.
without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis
with decompensated with chronic for use in combination with Ribavirin
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of VELAKAST is one tablet taken orally once daily with or without food. One tablet of VELAKAST contains 400 mg of sofosbuvir and 100 mg of velpatasvir. Table 5 shows the recommended treatment regimen and duration based on patient population. No Dosage Recommendations in Severe Renal Impairment and End Stage Renal Disease No dosage recommendation can be given for patients with severe renal impairment (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate [eGFR] less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) or with end stage renal disease (ESRD), due to higher exposures (up to 20-fold) of the predominant sofosbuvir metabolite.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
VELAKAST and ribavirin combination regimen is contraindicated in patients for whom ribavirin is contraindicated. Refer to the ribavirin prescribing information for a list of contraindications for ribavirin.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Serious Symptomatic Bradycardia When Sofosbuvir Is Coadministered with Amiodarone and Another HCV Direct Acting Antiviral Postmarketing cases of symptomatic bradycardia and cases requiring pacemaker intervention have been reported when amiodarone is coadministered with sofosbuvir in combination with daclatasvir or simeprevir. A fatal cardiac arrest was reported in a patient taking amiodarone who was coadministered a sofosbuvir-containing regimen (HARVONI (ledipasvir/sofosbuvir)). Bradycardia has generally occurred within hours to days, but cases have been observed up to 2 weeks after initiating HCV treatment. Patients also taking beta blockers, or those with underlying cardiac comorbidities and/or advanced liver disease may be at increased risk for symptomatic bradycardia with coadministration of amiodarone. Bradycardia generally resolved after discontinuation of HCV treatment. The mechanism for this effect is unknown.
Coadministration of amiodarone with VELAKAST is not recommended. For patients taking amiodarone who have no other alternative viable treatment options and who will be coadministered VELAKAST:
Counsel patients about the risk of symptomatic bradycardia.
Cardiac monitoring in an in-patient setting for the first 48 hours of coadministration is recommended, after which outpatient or self-monitoring of the heart rate should occur on a daily basis through at least the first 2 weeks of treatment. Patients who are taking VELAKAST who need to start amiodarone therapy due to no other alternative viable treatment options should undergo similar cardiac monitoring as outlined above.
Due to amiodarone’s long half-life, patients discontinuing amiodarone just prior to starting VELAKAST should also undergo similar cardiac monitoring as outlined above. Patients who develop signs or symptoms of bradycardia should seek medical evaluation immediately. Symptoms may include near-fainting or fainting, dizziness or lightheadedness, malaise, weakness, excessive tiredness, shortness of breath, chest pains, confusion, or memory problems Risk of Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Concomitant Use of VELAKAST with Inducers of P-gp and/or Moderate to Potent Inducers of CYP Drugs that are inducers of P-gp and/or moderate to potent inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4 (e.g., rifampin, St. John’s wort, carbamazepine) may significantly decrease plasma concentrations of sofosbuvir and/or velpatasvir, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect of VELAKAST. The use of these agents with VELAKAST is not recommended Risks Associated with Ribavirin and VELAKAST Combination Treatment If VELAKAST is administered with ribavirin, the warnings and precautions for ribavirin apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the ribavirin prescribing information for a full list of the warnings and precautions for ribavirin.
OVERDOSAGE
No specific antidote is available for overdose with VELAKAST. If overdose occurs the patient must be monitored for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with VELAKAST consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. Hemodialysis can efficiently remove the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir, GS-331007, with an extraction ratio of 53%. Hemodialysis is unlikely to result in significant removal of velpatasvir since velpatasvir is highly bound to plasma protein.
HOW SUPPLIED AND STORAGE
Each bottle contains 28 tablets and is closed with a child-resistant closure. Storage: Store below 30°C







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.