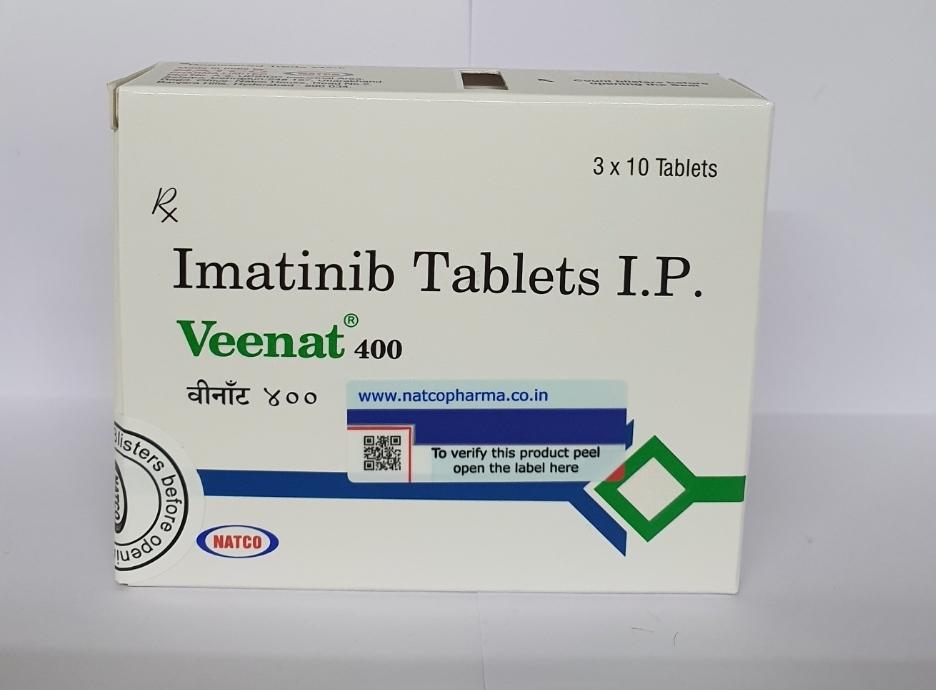
Enquire Veenat 400mg Imatinib tablets I.P
Veenat 400 mg is a relatively recent development of scientists. The active substance of this drug, Imatinib, is widely used as a cytotoxic agent. Its action is explained by the ability to block enzymes, which are the key to the rapid development of chronic myelogenous leukemia. This article gives an idea not only about the benefits of Veenat 400 mg in the therapy of blood cancer but also about the features of the development of the disease itself, which helps to fully understand the mechanism of action of the described drug.
VEENAT 400 MG (IMATINIB)
We present to your attention a brief description of Veenat 400:
The name of the commodity unit is Veenat 400.
The active substance of the drug is Imatinib (Imatinib mesylate).
Medicinal form – tablets.
The packing is 30 pieces.
The manufacturing company is India, Natco Pharma LTD.
Indications for use:
Chronic myelogenous leukemia at any stage is a slowly progressing development of malignant neoplasms in the hematopoiesis system. The most common CML occurs in elderly people.
Malignant stromal tumors, characterized as inoperable or metastatic.
Contraindications:
Veenat 400 mg is a drug that has a directional effect, but even this characteristic does not allow considering it absolutely safe, because at the moment the studies carried out have not touched some categories of patients, therefore the appointment is not recommended.
Children up to 3 years;
Pregnant women;
Nursing women;
Side Effects of Veenat 400 mg Imatinib
Side effect Imatinib can affect all body systems. Let’s describe the possible options:
Hematology. Increased toxicity in the form of cytopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, as well as suppression of bone marrow function.
Hepatology. Increased bilirubin, as well as transaminase.
Exchange of substances. Violation of the balance of potassium and sodium, anorexia, weight gain, increased quantitative indicators of uric acid, anorexia.
Water balance. Fluid retention, characterized mainly by clusters in the limbs, complications in the form of pleural or pericardial effusion, ascites, edema of the lungs or subcutaneous tissue.
GIT. Nausea, constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, indigestion, bleeding, abdominal pain.
Musculoskeletal system. Muscle and bone pain, muscle spasms, myalgia, arthralgia.
Respiratory system. A cough, susceptibility to infectious diseases (pharyngitis, pneumonia, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, etc.), dyspnea.
The nervous system. Frequent headaches, migraine, dizziness, insomnia, drowsiness, convulsions, fainting, depression, memory impairment, hemorrhage.
Cardiovascular system. Tachycardia, heart failure, pericarditis, arterial hypertension, cold extremities, hot flashes.
Skin covers. Itching, rash.
Urinary system. Frequent urination, kidney failure, kidney pain.
Organs of vision. Eye irritation, increased lacrimation, conjunctivitis, hemorrhage, glaucoma, edema (papillary, macular).
Reproductive system. Decreased potency, swelling of the scrotum, gynecomastia, pain in the nipples, enlargement of the mammary glands.
Other side effects. Anxiety, flu, fever.
Veenat 400 mg Uses:
For the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia, Veenat 400 mg is the main drug, so it can be used as a monotherapy. For treatment of malignant stromal tumors, this drug is used as an auxiliary drug, i.e. has a concomitant beneficial effect.
General recommendations contained in the instructions of Imatinib:
Doses over 600 mg are usually divided into two doses at regular intervals.
The drug is not intended for self-treatment. All appointments are made only by a qualified doctor. Unauthorized discontinuation is prohibited, as well as a reduction in the daily dose.
Continuous monitoring of treatment parameters is required. Timely detection of insufficient or excessive levels of Imatinib in the blood will help to correctly react and adjust the dose in order to avoid undesirable consequences. The compulsory procedure requires a complete clinical analysis of peripheral blood, bone marrow studies, and determination of the level of bilirubin and transaminases.
The dosage of the drug depends on many factors, for example, on the disease, its stage, the experience of treatment with other drugs, the presence, and nature of side effects, etc.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.